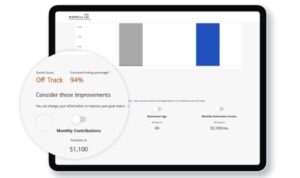
In the financial world, understanding the differences between various investment vehicles is crucial for making informed decisions. When it comes to collective investment trusts and mutual funds, many investors find themselves pondering which option aligns best with their financial goals. Both options allow individuals to pool their resources for investment, but they come with distinct features and benefits that can significantly impact long-term returns and accessibility.
As we explore collective investment trusts and mutual funds, we’ll unravel the key distinctions in terms of structure, taxation, and fees, while also examining the advantages and disadvantages of each. This discussion aims to clarify these investment choices, empowering you to navigate the investment landscape more confidently.
The story of technology is one of relentless innovation, creativity, and progress. It is an ever-evolving narrative that has shaped the very fabric of human existence. From the early days of simple tools to the sophisticated digital age we live in today, the evolution of technology has been marked by significant milestones that have transformed the way we interact with the world.

1. The Dawn of Technology
In the beginning, technology was a means of survival. Our ancestors created rudimentary tools from stone, wood, and bone, allowing them to hunt, gather, and build shelters. This era, often referred to as the Stone Age, laid the foundation for future innovations. The ability to make fire, for example, not only provided warmth but also revolutionized cooking, leading to improved nutrition and health.
2. The Agricultural Revolution
Fast forward to around 10,000 BC, and we find ourselves in the midst of the Agricultural Revolution. This period marked a significant shift from nomadic lifestyles to settled farming communities. The domestication of plants and animals led to the development of agriculture, which in turn spurred advancements in technology. The invention of the plow, irrigation systems, and storage facilities were critical in enhancing productivity and supporting larger populations.
3. The Age of Metals
The discovery of metals, particularly bronze and iron, ushered in what is known as the Bronze Age and the Iron Age. These new materials allowed for the creation of stronger tools and weapons, fundamentally changing societies. With improved agricultural tools, people could cultivate land more efficiently, leading to surplus food and the growth of civilizations. Additionally, metalworking led to the rise of trade, as societies exchanged resources and ideas.
4. The Rise of Civilizations
As civilizations formed, so did the need for more complex technologies. The invention of writing around 3200 BC in Mesopotamia was a pivotal moment in history. It enabled the recording of information, allowing for the administration of growing populations and the preservation of knowledge. This era also saw the construction of monumental architecture, such as the pyramids of Egypt and the ziggurats of Mesopotamia, showcasing the advanced engineering and organizational skills of these ancient societies.
5. The Renaissance and the Age of Enlightenment
The Renaissance, beginning in the 14th century, marked a renewed interest in science, art, and exploration. Innovative thinkers, such as Leonardo da Vinci and Galileo Galilei, pushed the boundaries of knowledge and technology. The invention of the printing press by Johannes Gutenberg in the 15th century revolutionized the dissemination of information, making books more accessible and fostering literacy. This period set the stage for the Age of Enlightenment, where reason and scientific thought further accelerated technological advancements.
6. The Industrial Revolution
In the late 18th century, the Industrial Revolution transformed economies and societies on an unprecedented scale. The shift from agrarian societies to industrial powerhouses brought about significant technological innovations, including the steam engine, textile machinery, and the telegraph. Factories sprung up, leading to urbanization and a new workforce. This era emphasized mass production and efficiency, changing the dynamics of labor and commerce forever.
7. The Age of Electricity and Communication
The late 19th and early 20th centuries witnessed a surge in electrical innovations. Thomas Edison’s invention of the electric light bulb and Nikola Tesla’s work on alternating current revolutionized how we lived and worked. The invention of the telephone by Alexander Graham Bell and the radio fundamentally changed communication, connecting people across distances like never before. This era laid the groundwork for the interconnected world we experience today.
8. The Digital Revolution
The late 20th century heralded the Digital Revolution, a period defined by the rise of computers and the internet. The introduction of personal computers in the 1970s and 1980s changed the landscape of information technology, making computing accessible to the average person. The advent of the internet in the 1990s transformed how we communicate, share information, and conduct business. Social media platforms emerged, creating new avenues for interaction and community.
9. The Era of Artificial Intelligence
As we entered the 21st century, artificial intelligence (AI) began to take center stage. AI technologies, such as machine learning and natural language processing, are now integral to various sectors, from healthcare to finance. The ability of machines to learn from data and make decisions has sparked both excitement and debate about the future of work and ethics. AI has already begun to automate tasks, leading to enhanced efficiency but also raising questions about job displacement and privacy.
10. The Future of Technology
Looking ahead, the future of technology is filled with possibilities. Emerging fields such as quantum computing, biotechnology, and renewable energy promise to reshape our world once again. As we grapple with challenges like climate change and resource scarcity, technology will play a critical role in creating sustainable solutions. The integration of technology into everyday life will continue to evolve, with smart devices and the Internet of Things (IoT) becoming increasingly commonplace.
Conclusion
The evolution of technology is a testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of progress. Each era has built upon the discoveries of the past, leading us to where we are today. As we navigate the complexities of modern technology, it is essential to remain mindful of its impact on society and the environment. The journey of technology is far from over, and the future holds exciting prospects that will undoubtedly shape our world in ways we cannot yet imagine.

Top FAQs
What are the primary differences between a collective investment trust and a mutual fund?
The primary differences lie in their regulatory framework, management structure, and cost. Collective investment trusts are typically less regulated and may have lower fees, while mutual funds are subject to more stringent regulatory requirements and often have higher management costs.
Can individual investors access collective investment trusts?
Generally, individual investors do not have direct access to collective investment trusts, as they are mainly offered through retirement plans or institutional investors. However, they can participate indirectly through an employer-sponsored plan.
Are the tax implications different for collective investment trusts and mutual funds?
Yes, there can be differences in tax implications. Collective investment trusts may have fewer taxable events compared to mutual funds, which can lead to more favorable tax treatment for certain investors.
Which investment option is more suitable for long-term investing?
The choice between the two depends on individual circumstances. Mutual funds are often more suitable for retail investors seeking diversification and professional management, while collective investment trusts may benefit institutional investors looking for lower fees and specific investment strategies.

How do fees compare between collective investment trusts and mutual funds?
Collective investment trusts generally have lower fees than mutual funds due to less regulation and operational costs, making them an attractive option for cost-conscious investors.